Introduction
In the world of chemical and petrochemical industries, catalyst unloading is a critical task for maintaining efficiency and productivity in reactors.
Within the catalyst handling process, the first step is catalyst unloading.
The two methods we use at Lagupres are Suction Unloading and Gravity Unloading.
In this article we will explain in detail the two methods, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to optimise their implementation to ensure a smooth and efficient operation.
Catalyst unloading by suction
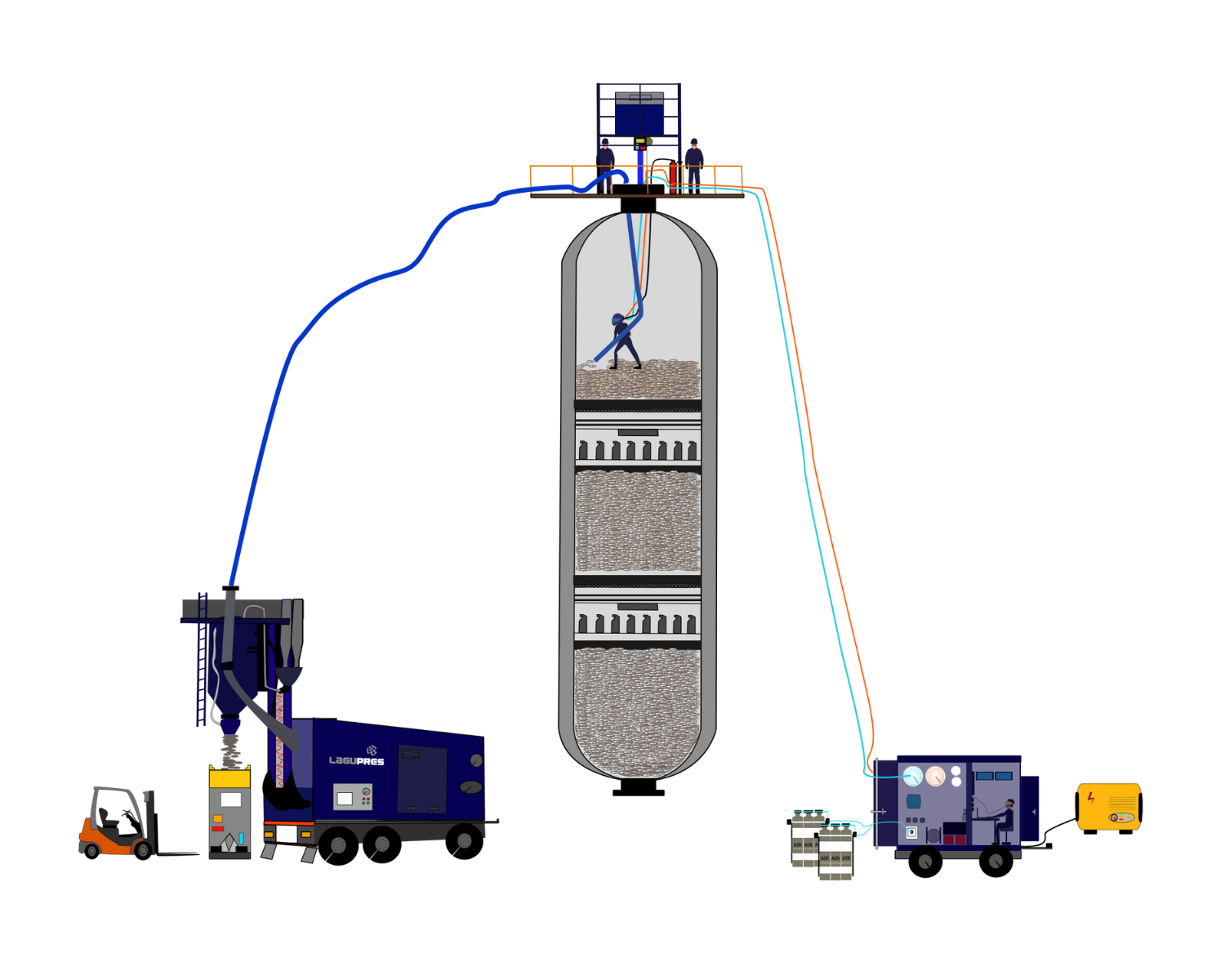
Catalyst unloading by suction uses a specially designed vacuum system to suck out the old catalyst. This suction system is able to remove catalyst residues efficiently and accurately.
Advantages:
Selective extraction
The unloading by suction allows a selective removal of the catalyst, avoiding unnecessary damage to the reactor.
Increased efficiency
This method is fast and efficient, allowing faster catalyst replacement and reducing downtime in the industrial production process.
Disadvantages::
Initial cost
The implementation of a vacuum system may require a more significant initial investment in specialised equipment and technology.
Technical requirements
Trained and knowledgeable personnel are required to properly operate the suction equipment and ensure accurate extraction without compromising the integrity of the reactor.
Technical requirements
In some industrial applications, reactors can operate in inert atmospheres, such as nitrogen or argon. In such cases, unloading by suction presents additional challenges due to the lack of oxygen in the environment. To ensure the safety of personnel, the use of appropriate personal protective equipment, such as semi-autonomous breathing helmets, is required.
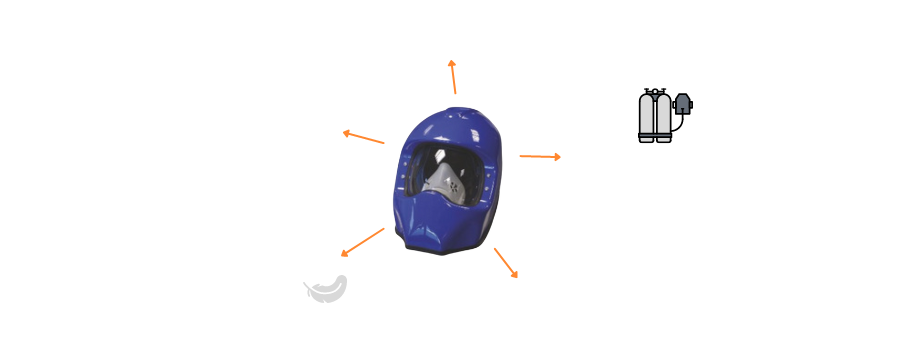
Use of the Semi-Autonomous Breathing Helmet:
The semi-autonomous breathing helmet is essential personal protective equipment for workers performing unloading by aspiration in inert atmospheres. These helmets are designed to provide a continuous supply of clean air to the wearer, allowing them to breathe safely while operating in oxygen-deficient environments. These helmets are equipped with integrated air supply systems, which may include compressed air cylinders or external air supply systems connected to a central source.
The semi-autonomous respirator helmet provides several advantages in unloading by suction in inert atmospheres:
Continuous supply of fresh air
The helmet ensures that workers have a constant supply of clean air, regardless of atmospheric conditions or the composition of the air in the reactor. This ensures the safety and health of personnel during the entire unloading process.
Protection against toxic gases
In some cases, reactors may contain toxic gases or vapours that must be evacuated during unloading. Semi autonomous breathing helmets, together with appropriate filters, can provide protection against these gases, preventing exposure and possible adverse health effects.
Freedom of movement
The semi-autonomous breathing helmets are designed to be lightweight and comfortable to wear, allowing workers to move easily during unloading. This is especially important in industrial environments where mobility is crucial to perform tasks efficiently and safely.
Training and know-how
It is essential that personnel involved in unloading by aspiration in inert atmospheres receive adequate training in the use and maintenance of semi-autonomous breathing apparatus. This will ensure correct operation of the equipment and effective protection for the workers involved.
In conclusion, in cases where unloading by suction takes place in reactors located in inert atmospheres, the use of semi-autonomous breathing helmet is essential to ensure the safety and health of workers. These units provide a continuous supply of fresh air and protection against toxic gases, allowing catalyst unloading to be carried out safely and efficiently in challenging industrial environments.
Catalyst Unloading by gravity
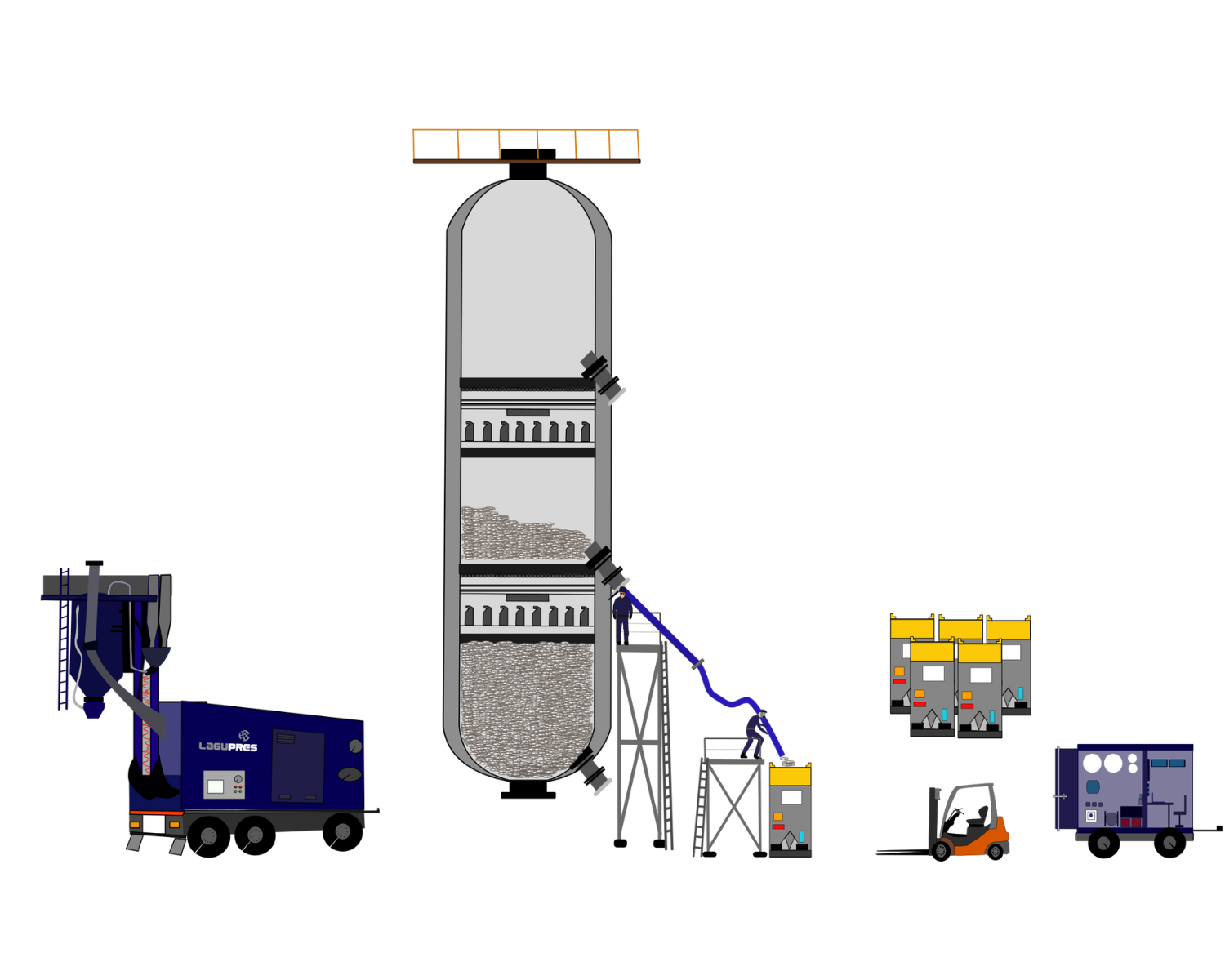
Gravity unloading is a less aggressive technique. Reactor entry is eliminated and catalyst breakage is reduced.
For gravity unloading, the reactor must have an unloading port.
There are some drawbacks to Catalyst Unloading by gravity.
If the catalyst is agglomerated, unloading by gravity is not possible. In this case, at Lagupres, we use Carbodump technology. Carbodump consists of compressed CO2 cartridges that expand and decompress the agglomerated catalyst.
In addition, gravity unloading is normally followed by a suction process to remove debris that has not “fallen” on its own feet, usually in the distance from the bottom of the bed to the unloading mouth.

